- Our Products
- Upper Extremity
 Amadeo Finger-Hand-Rehabilitation
Amadeo Finger-Hand-Rehabilitation
Amadeo is giving hands back their grip and fingers their finesse. Patients who are barely able or unable to grasp can perform hundreds of robot-assisted grasping movements. It won’t train a new Mozart. But it will help patients return to the piano, handwriting Christmas cards, and grabbing life firmly by the horns.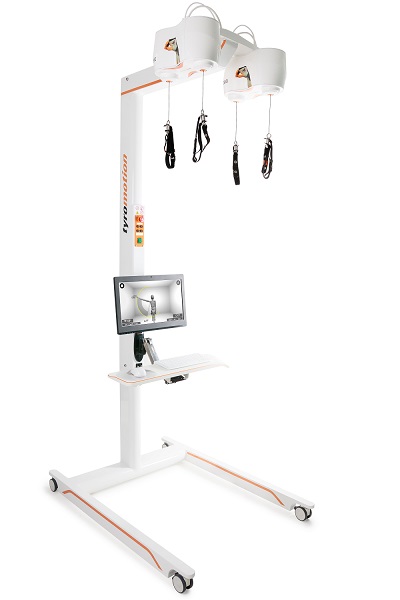 DiegoShoulder-Arm-Rehabiliation
DiegoShoulder-Arm-Rehabiliation
Diego is designed to strengthen what’s important. Whether proximal or distal training, Diego purposefully supports the rehabilitation of natural motion, allows the handling of everyday objects to be relearned, and is usable by adults and children alike.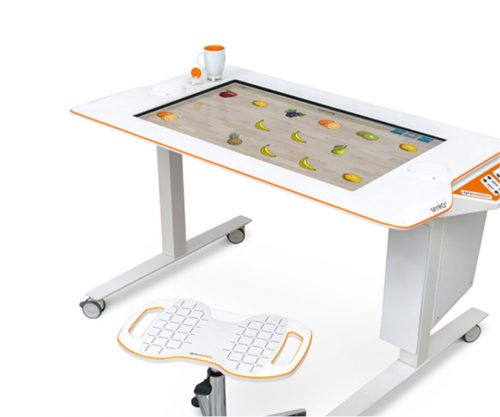 Myro Interactive and task-specific therapy
Myro Interactive and task-specific therapy
Myro is made for making humans get better! The sensor-based surface enables task-oriented rehabilitation with real objects, trains the patient’s cognitive abilities, and improves motor abilities of the upper extremity.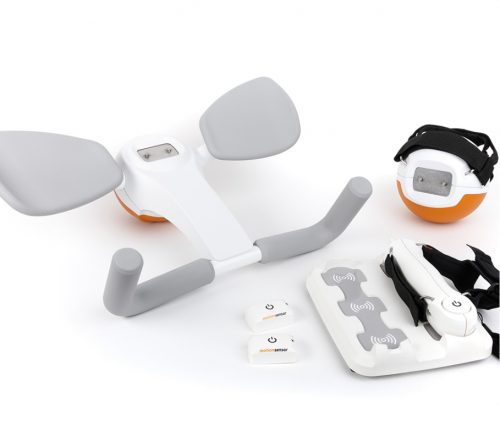 Pablo Upper Extremity Rehabilitation
Pablo Upper Extremity Rehabilitation
As a multifunctional rehabilitation device with comprehensive accessories, Pablo enhances classical therapy exercises with biofeedback, objective assessments, and gamification. It won´t train the next Picasso. But it will help patients to take back control of their lives.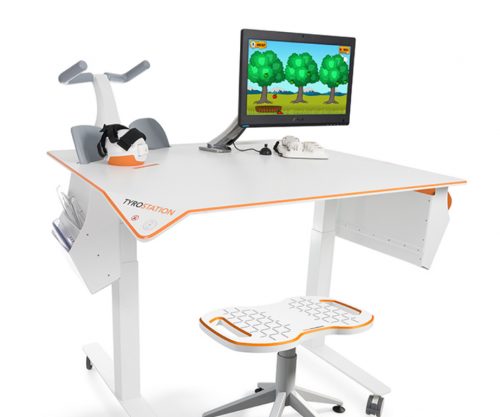 Tyrostation The perfect therapy setting
Tyrostation The perfect therapy setting
The Tyrostation is home to all components of Pablo and Tymo and provides ergonomic adaptability for patients. Sometimes, it´s about the little things in life – or therapy.
- Lower Extremity
 LexoGait and Locomotion
LexoGait and Locomotion
Lexo is a revolutionary gait trainer and impresses with fast setup, high patient activity and optimal trunk support. It encourages active participation and enables therapists to focus fully on their patients.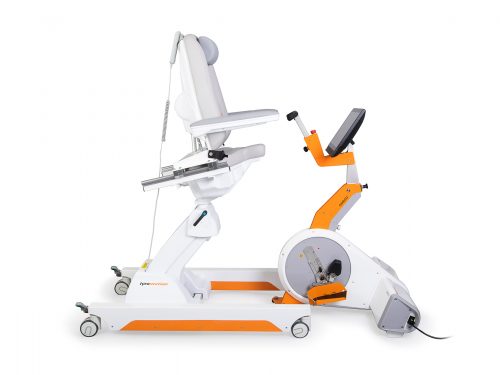 Omego Plus Gait training for the goals across all phases
Omego Plus Gait training for the goals across all phases
More than just a therapy bike! Omego Plus combines uni- and bilateral leg training, leg press, stepper, cycling & foot lift training in one device. Stride stronger with Omego Plus! Tymo Balance training and postural control
Tymo Balance training and postural control
Small but powerful! Tymo is a versatile measurement and therapy system for the whole body. In addition to the standing position, Tymo offers a wide range of options for maximum variety during therapy.
- MTT-Line
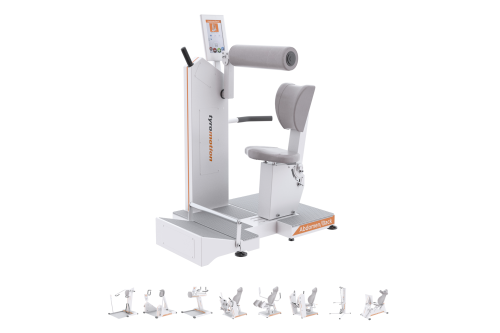 MTT-LineMedical training therapy
MTT-LineMedical training therapy
Get back in the game with the MTT-Line! The Medical Training Therapy devices are specifically designed to strengthen the six major muscle groups of the human body. Barrier free and maximum adjustability make the devices accessible for all types of patients.
- Software
 Maya Therapy Platform
Maya Therapy Platform
Maya reduces paperwork, standardizes documentation, and automates reporting, making administration effortless and efficient. Designed for therapists to work wonders!
- Upper Extremity
Rehabilitation
Advanced Rehabilitation Technology: Improving Life After Stroke
13. December 2021 ● 4 min. Reading time
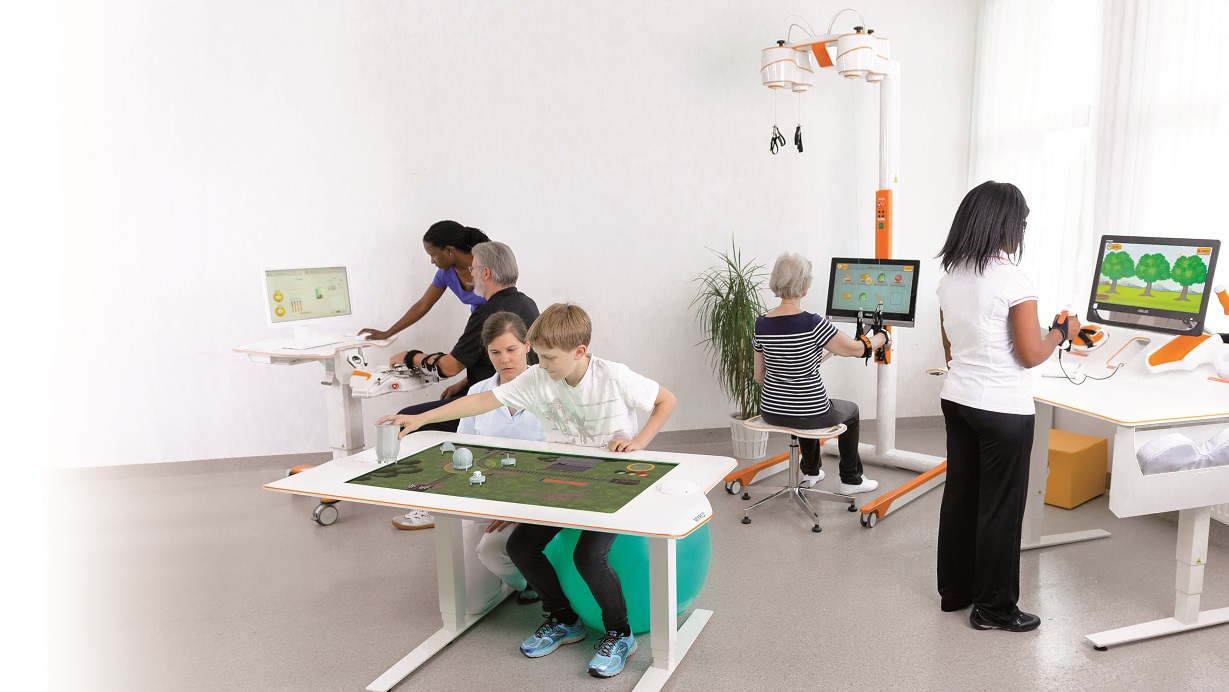

Advanced rehabilitation technology addresses the lack of motivation that can stand in the way of recovery. Using robot-assisted therapies, virtual reality (VR), and Gamification, therapists leverage the latest technologies to help patients rehabilitate their extremities.
Upping the Game for Upper Extremity Rehabilitation
Neurological damage can lead to spasticity or muscle atrophy. Spastic paralysis can affect individual muscles or entire areas of the body. The extent of the paralysis depends on which areas of the brain or spinal cord are damaged. Impaired motor function prevents people from performing activities essential to their independence. Writing, typing, or cooking may be difficult.
A fundamental goal of post-stroke rehabilitation is to optimize the functional use of the upper extremities. PT and OT exercises can help to decrease symptoms like tight and stiff muscles. Robot-assisted and VR-enabled devices also can help to reduce symptoms and are motivating.
With a Little Help from My Friends
Robot-assisted devices take a playful approach to upper extremity rehabilitation therapy that is both motivating and results-driven. Benefits include:
- Data-informed treatment plans. Robotic-assisted devices provide objective data that occupational and physical therapists analyze and use to shape their interventions. With data-informed treatment plans, therapists can prescribe more meaningful, goal-oriented tasks that accelerate and enhance recovery.
- Increased intensity and accuracy of exercises. With robotic-assisted devices, therapists can increase the frequency, dose, and intensity of therapeutic exercises. These devices also help ensure the accuracy of exercises by decreasing the chances of improper patient performance.
- Access to data. As patients continue to progress, robotic-assisted devices provide instant and concrete evidence of their continued progress. This information also helps demonstrate global improvements that can show patients how far they have come.
It's Not All Fun and Games
A study has found that when a patient enjoys an activity, the burden of recovery can be temporarily forgotten. Instead of simple sets of exercises, gamified devices engage and distract patients from the pain and hard work of rehabilitation.
VR-enabled devices present patients with virtual tasks, such as picking fruit or hanging laundry. The movements mimic their actual life. VR applications are not only engaging, but they are also helpful in reengaging the muscles and joints needed to perform such tasks.
Lifting Up the Lower Extremities
Stroke can also affect a person’s motor function in their legs, leaving them with limited or no ability to walk. Therapists aim to get patients walking again by improving their lower extremity strength, speed, rhythm, and cadence. Gait rehabilitation is a mainstay of post-stroke recovery and helps to reduce the risk of falls. It helps to improve a patient’s balance and to regain walking ability, distance, and speed.
Game-Changing Gait Therapy
Traditional gait therapy challenges and encourages patients. But the exercises often require a lengthy setup process, risky patient transfer, and hands-on assistance. Therapy can also result in compensation instead of recovery. With advanced rehabilitation therapy, therapists and patients gain repetitions, attention, and precision that helps them maximize treatment.
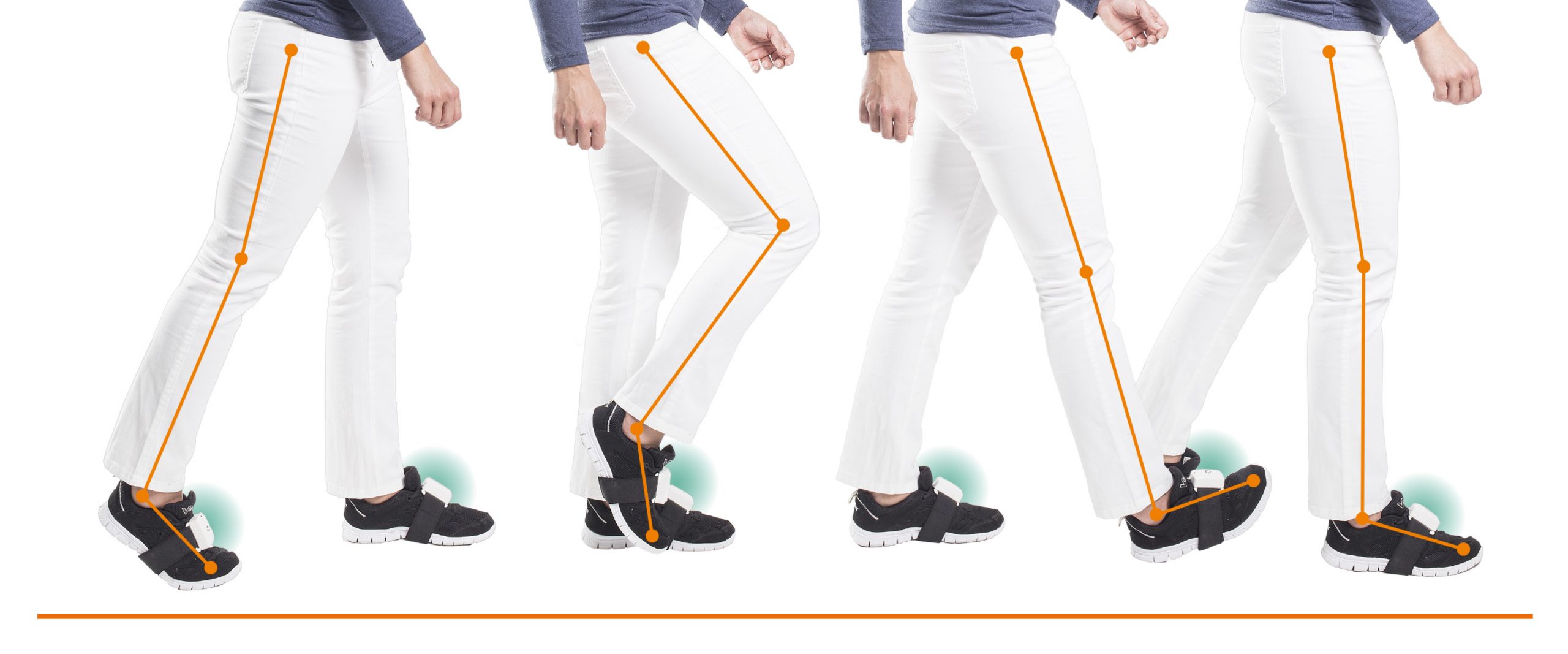
Some devices use sensors to analyze a patient’s gait patterns more objectively and accurately. The device also uses analyzed data to personalize its training module to each patient. The objective data – such as cadence, stride length, gait cycle, and foot-floor angles – helps the therapist create a more visual and precise picture of how their patient is improving. This encouraging information can inspire a cycle of motivation that makes a marked difference in patient recovery.
Building the Foundation Through Stability and Coordination
A majority of stroke survivors endure some functional disability that increases their likelihood of falling. A combination of muscle weakness, unbalanced weight distribution and lack of equilibrium contribute to instability leading to post-stroke falls. For example, patients who are unstable and uncoordinated experience problems with transitions from sitting to standing.
Computer-assisted tools can help retrain the brain and help patients regain stability and coordination. With Tymo, for example, therapists gain a better understanding where the visual, vestibular, and somatosensory systems deficiencies lie. Then, they can fine tune prescribed therapies to target specific functions.
Advanced rehabilitation technologies use attention-grabbing games that facilitate the repetitive exercises required to relearn lost movements. These therapeutic games can boost self-esteem and self-confidence, enhancing the trajectory of patient recovery.
Recovery is Different for Every Patient
While some stroke survivors overcome obstacles with more ease than others, the healing journey is almost always challenging. That’s why seeking the right type of care makes all the difference. With its personalized, motivational approach, advanced rehabilitation technology has revolutionized post-stroke therapy. Still, a therapist will always be by your side to adapt technologies according to the patient´s needs. Technology will never be able to replace humans in rehabilitation, but it can make certain tasks easier for the therapist and the patient.
You might also be interested in
4. April 2023
Health
Rehabilitation
Stroke nutrition guidelines for optimal health
Nutrition as the key part in health and well-being of stroke survivors A healthy, balanced …
21. March 2023
Rehabilitation
Kinesio taping in neurology as a useful therapy supplement
The Kinesio tape and its usefulness in neurological therapy What was originally known only from …
7. March 2023
Rehabilitation
Exercises against freezing of gait in Parkinson’s disease
When the legs freeze – how does the symptom “Freezing of Gait” manifest itself? Parkinson’s …



 Contact
Contact 

 Contact
Contact