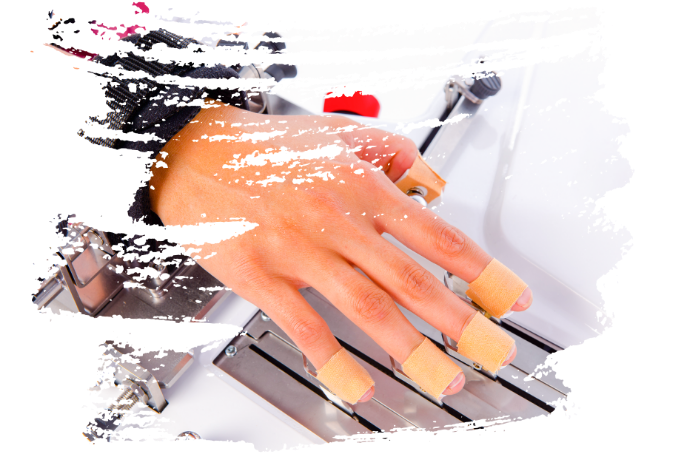
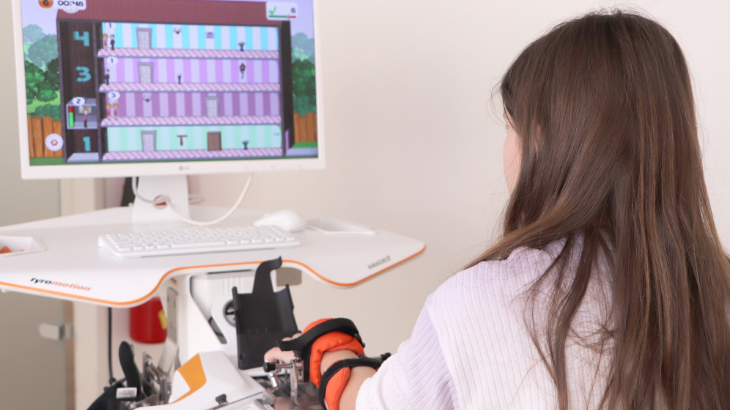
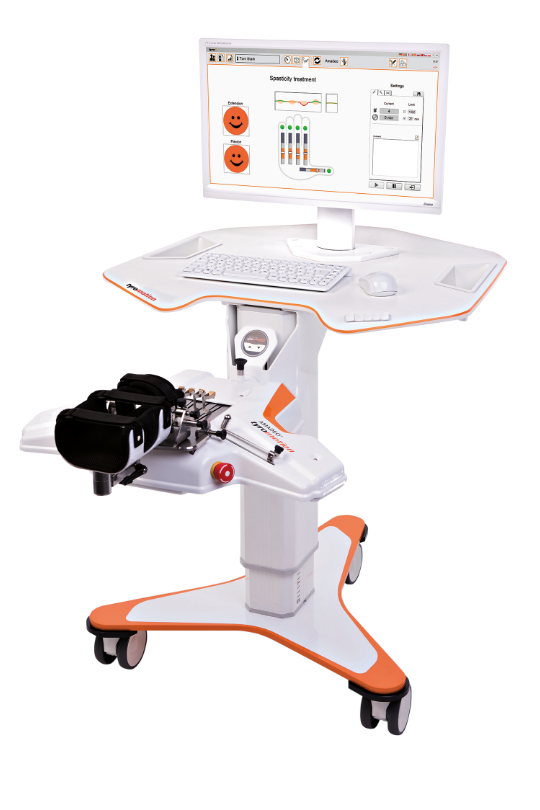
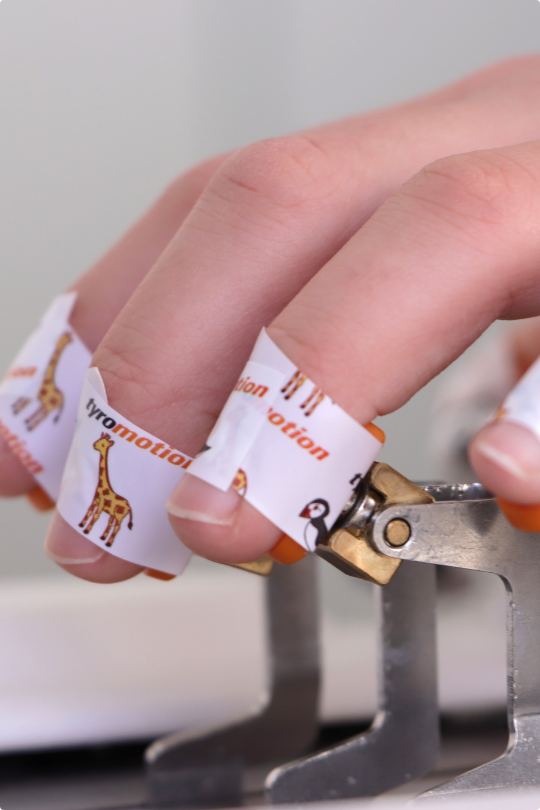
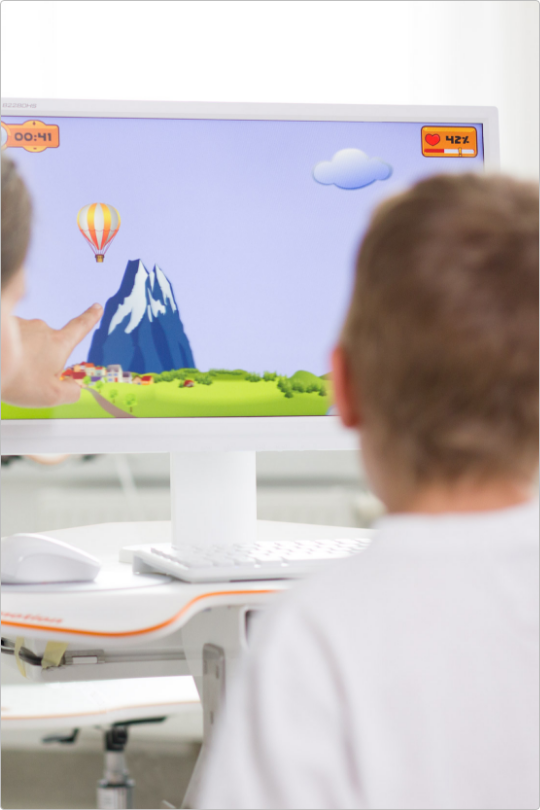
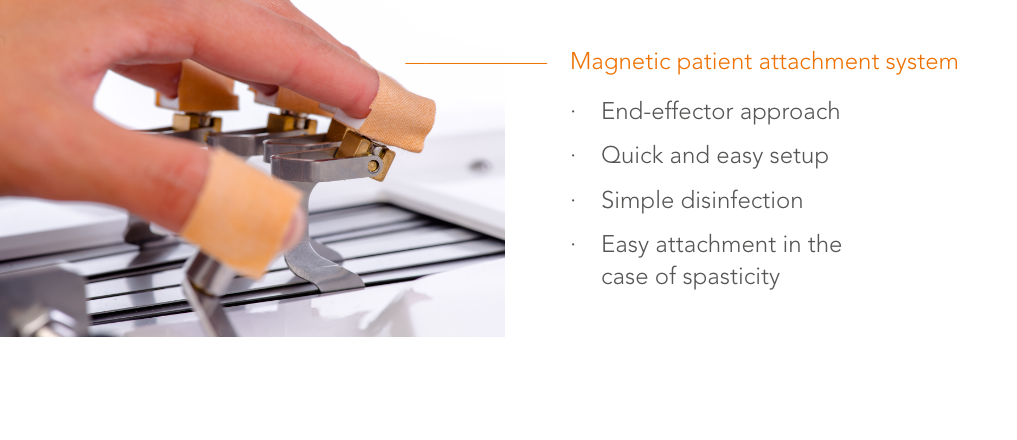
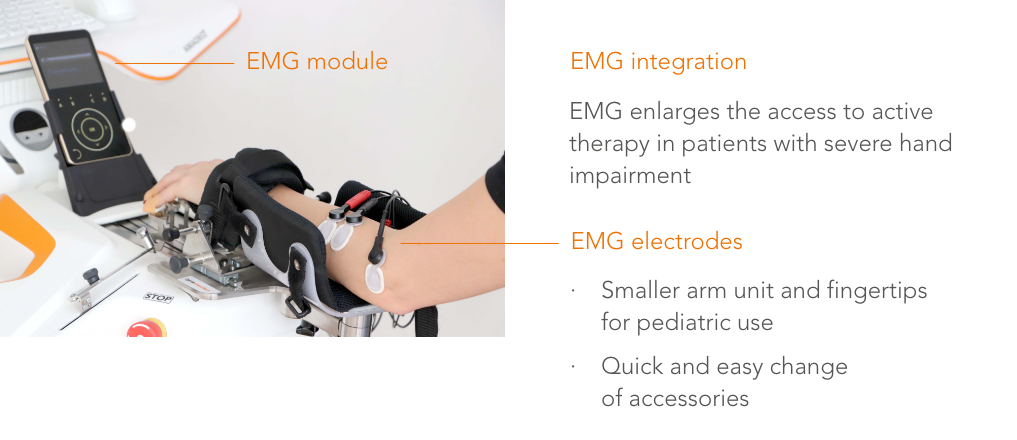
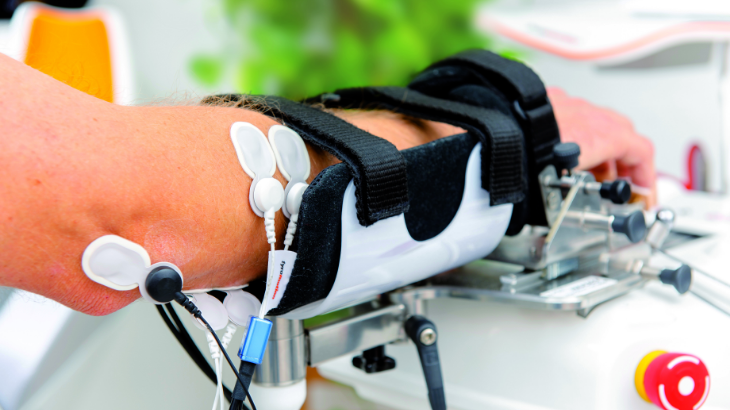
"Robotic training yields improvement of hand motor performance by restoring hand motor control."
Calabrò RS, Accorinti M, Porcari B, Carioti L, Ciatto L, Billeri L, Andronaco VA, Galletti F, Filoni S, Naro A. Verbessert die robotische Rehabilitation der Hand die motorische Funktion durch Wiederherstellung der interhemisphärischen Konnektivität nach chronischem Schlaganfall? Ermutigende Daten aus einer randomisierten klinischen Studie. Clin Neurophysiol. 2019 May; 130(5):767-780.
"In subjects with subacute stroke, robotic-assisted therapy using a set of robotic and sensor-based devices significantly improved UL motor function, activities, and participation to the same extent as a similar amount of conventional therapy."
Aprile I, Germanotta M, Cruciani A, Loreti S, Pecchioli C, Cecchi F, Montesano A, Galeri S, Diverio M, Falsini C, Speranza G, Langone E, Papadopoulou D, Padua L, Carrozza MC; FDG Robotic Rehabilitation Group. Robotische Rehabilitation der oberen Gliedmaßen nach Schlaganfall: Eine multizentrische, randomisierte klinische Studie. J Neurol Phys Ther. 2020 Jan;44(1):3-14.
"Task-oriented VR-based robotic rehabilitation enhanced not only motor function in the paretic arm but also global and specific cognitive abilities in post-stroke patients."
Torrisi M, Maggio MG, De Cola MC, Zichittella C, Carmela C, Porcari B, la Rosa G, De Luca R, Naro A, Calabrò RS. Über die motorische Erholung nach einem Schlaganfall hinaus: Die Rolle der Hand-Roboter-Rehabilitation plus virtuelle Realität bei der Verbesserung der kognitiven Funktion. J Clin Neurosci. 2021 Oct;92:11-16.