- Our Products
- Upper Extremity
 Amadeo Finger-Hand-Rehabilitation
Amadeo Finger-Hand-Rehabilitation
Amadeo is giving hands back their grip and fingers their finesse. Patients who are barely able or unable to grasp can perform hundreds of robot-assisted grasping movements. It won’t train a new Mozart. But it will help patients return to the piano, handwriting Christmas cards, and grabbing life firmly by the horns.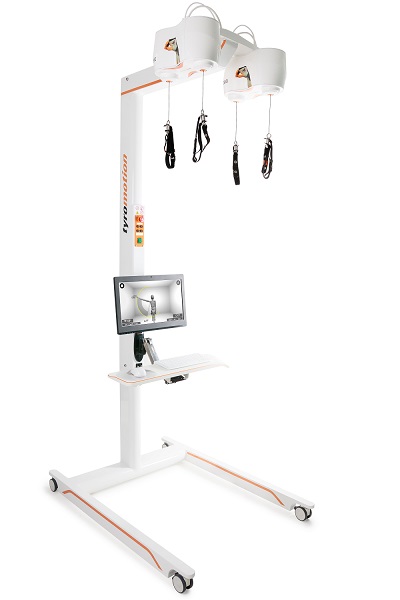 DiegoShoulder-Arm-Rehabiliation
DiegoShoulder-Arm-Rehabiliation
Diego is designed to strengthen what’s important. Whether proximal or distal training, Diego purposefully supports the rehabilitation of natural motion, allows the handling of everyday objects to be relearned, and is usable by adults and children alike.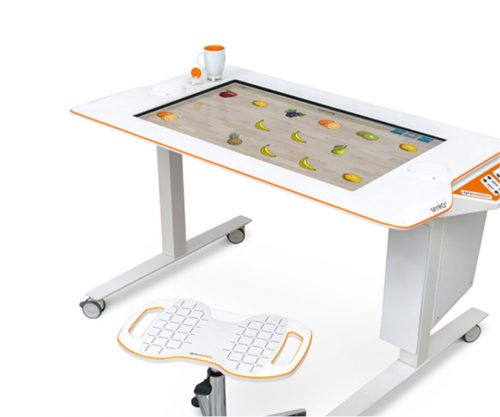 Myro Interactive and task-specific therapy
Myro Interactive and task-specific therapy
Myro is made for making humans get better! The sensor-based surface enables task-oriented rehabilitation with real objects, trains the patient’s cognitive abilities, and improves motor abilities of the upper extremity.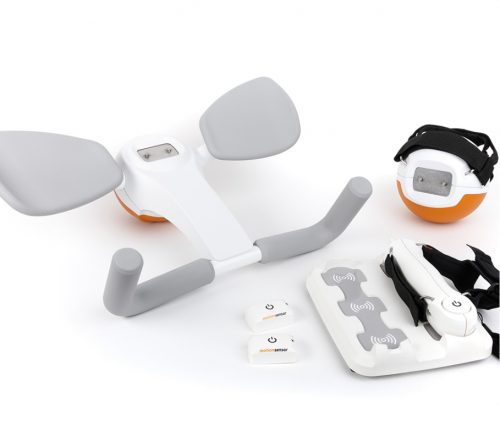 Pablo Upper Extremity Rehabilitation
Pablo Upper Extremity Rehabilitation
As a multifunctional rehabilitation device with comprehensive accessories, Pablo enhances classical therapy exercises with biofeedback, objective assessments, and gamification. It won´t train the next Picasso. But it will help patients to take back control of their lives.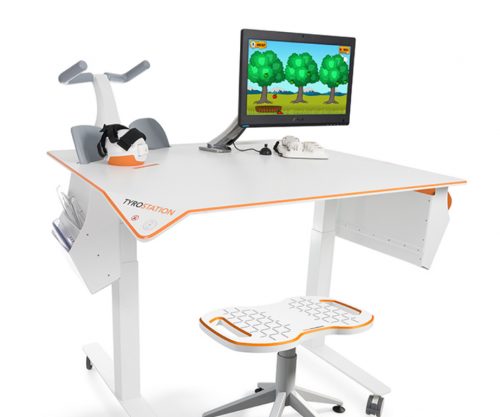 Tyrostation The perfect therapy setting
Tyrostation The perfect therapy setting
The Tyrostation is home to all components of Pablo and Tymo and provides ergonomic adaptability for patients. Sometimes, it´s about the little things in life – or therapy.
- Lower Extremity
 LexoGait and Locomotion
LexoGait and Locomotion
Lexo is a revolutionary gait trainer and impresses with fast setup, high patient activity and optimal trunk support. It encourages active participation and enables therapists to focus fully on their patients.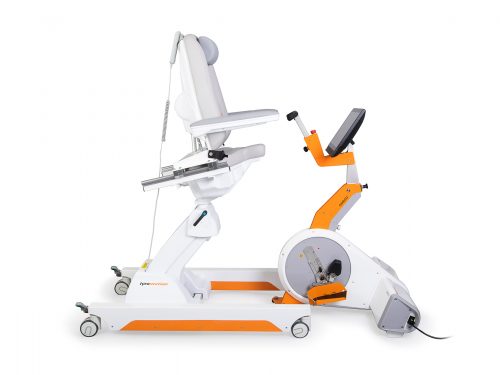 Omego Plus Gait training for the goals across all phases
Omego Plus Gait training for the goals across all phases
More than just a therapy bike! Omego Plus combines uni- and bilateral leg training, leg press, stepper, cycling & foot lift training in one device. Stride stronger with Omego Plus! Tymo Balance training and postural control
Tymo Balance training and postural control
Small but powerful! Tymo is a versatile measurement and therapy system for the whole body. In addition to the standing position, Tymo offers a wide range of options for maximum variety during therapy.
- MTT-Line
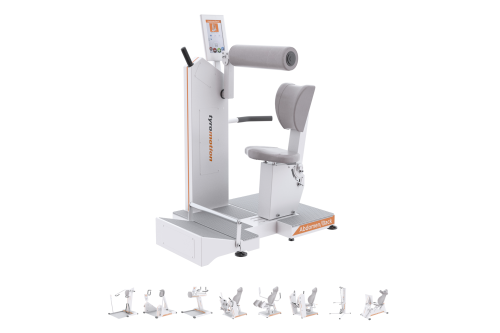 MTT-LineMedical training therapy
MTT-LineMedical training therapy
Get back in the game with the MTT-Line! The Medical Training Therapy devices are specifically designed to strengthen the six major muscle groups of the human body. Barrier free and maximum adjustability make the devices accessible for all types of patients.
- Software
 Maya Therapy Platform
Maya Therapy Platform
Maya reduces paperwork, standardizes documentation, and automates reporting, making administration effortless and efficient. Designed for therapists to work wonders!
- Upper Extremity
MTT Study
Stroke patients can experience a reduction in muscle strength and range of motion, a loss of sensory and motor coordination as well as abnormal muscle tone. This may lead to difficulties in postural control and reduced balance function. The results are an increased risk of falling, increased economic costs and hospitalization period as well as loss of participation and quality of life.
Muscle strength is one of the parameters closely related to functional balance and gait performance. In addition to rehabilitation with sensory and robotic devices, strength training plays a crucial role in building and maintaining muscle strength in the rehabilitation process. A study from Son et al. (2014) demonstrates that muscle strength training across multiple joints of the lower limbs enhances dynamic balance function of stroke patients. The researchers conclude that Medical Training Therapy (MTT) offers a viable option for improving patients’ dynamic balance, postural control, independence, and gait after stroke.
The Tyromotion MTT-Line provides a set of medical training therapy devices for the six major muscle groups of the human body. The lower extremity devices LEG EXTENSION/CURL, ADDUCTION/ABDUCTION, LEG PRESS, and the PULLEY FREE STANDING can be used to build up strength in the lower limb, fostering functional balance.



 Contact
Contact 


 Contact
Contact